
Shares outstanding and floating stock are two types of share-number metrics that are important for investors. Although they both refer to all classes of a company’s common stock (as opposed to preferred stock), these two metrics are inherently different. Shares outstanding (or outstanding shares) are any shares that are held by shareholders and company insiders. Floating shares indicate the number of shares actually available for trading. So far, we’ve focused on shares outstanding, whether basic or diluted, at a fixed point in time. In SEC filings, companies will report the total number of shares outstanding on a given day, but in their quarterly and annual figures they must also offer the weighted average shares shares outstanding formula outstanding.
Shares Outstanding vs. Floating Stock: What’s the Difference?
Assume that Company A has 100 million shares outstanding and a trading price of $10. It also has 10 million stock options outstanding with an exercise price of $5. In other words, the treasury stock method accounts for the cash that will come in from option and warrant exercise, and assumes that the cash received will offset a portion of the shares issued. For most companies, the number of authorized shares well exceeds the shares outstanding. In addition, most public companies don’t need to issue more shares, at least in the number required to bump up against the authorized maximum.
Editorial integrity
- Floating stock, which is also known as a company’s float, refers to the number of shares a company actually has available to trade in the open market.
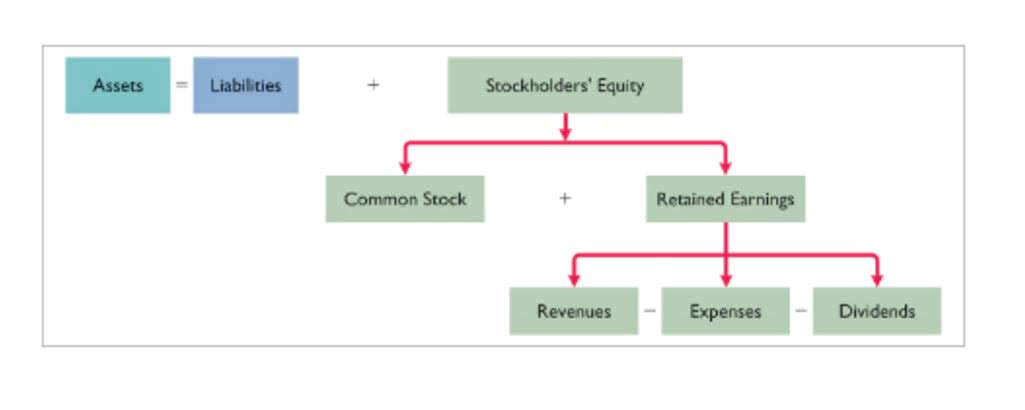
- Outstanding shares also include any blocks of stock held by institutional investors, such as mutual or pension fund companies.
- Those instruments can be “in the money” if the exercise price — the price designated for the stock by the option or warrant — is below the stock’s trading price.
- Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the company’s share price by its shares outstanding.
- Furthermore, by identifying the number of restricted shares versus the number of shares in the float, investors can gauge the level of ownership and autonomy that insiders have within the company.
The reason What is bookkeeping for that is that most public companies have instruments that provide for shares to be issued in the future. These instruments include stock options, stock warrants, and convertible debt. In a 1-for-2 reverse split, however, the number of shares is divided by two, while the share price doubles. Reverse stock splits often happen when a company needs to keep its share price above a certain level in order to remain in compliance with an exchange’s listing requirements. While a company has a certain number of outstanding shares, not all of those shares are available for trading, since they may be closely held by some (large) investors.

How to Derive Outstanding Shares
By contrast, many older stalwart companies are likely to have a number of shares outstanding that matches its number of shares fully diluted. Moreover, the number of shares outstanding is extremely useful when monitoring how a company conducts its business, as things like stock splits also affect share numbers. Several factors can cause a company’s number of outstanding shares to rise or fall, with one of the most common being stock splits. The purpose of the repurchase can also be to eliminate the shareholder dilution that will occur from future ESOs or equity grants. While outstanding shares are a determinant of a stock’s liquidity, the latter is largely dependent on its share float.
- Generally speaking, stocks with smaller floats will experience more volatility than those with larger floats.
- A company’s outstanding shares may change over time because of several reasons.
- Authorized shares represent the third share-number metric that investors often look at to get a comprehensive overview of a company’s stock shares.
- You can compare the differences between the figures on specific dates of the filings to find the change in outstanding shares.
- Heavy trading by closely held shareholders could also affect the stock’s weighting impact in free float capitalization indexes.
- Shares outstanding refers to the number of shares of common stock a company has issued to investors and company executives.
Denoting the greatest proportion of stocks trading on the exchanges, the float consists of regular shares that many of us will hear or read about in the news. A https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc company’s number of shares outstanding is used to calculate many widely used financial metrics. Market capitalization — share price times number of shares outstanding — and EPS are both computed using a company’s number of outstanding shares. The number of shares outstanding consists of shares held by institutions, restricted shares held by company insiders, and shares available for investors to buy and sell on the open market. Authorized shares represent the third share-number metric that investors often look at to get a comprehensive overview of a company’s stock shares.

